- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming»
- Computer Programming Tutorials
Complete Java Iterator tutorial with example codes | How to use Java Iterator
Java iterator is an interface of java collection framework. Object of java iterator is used to traverse through all the elements of a collection regardless of its specific implementation. It is very easy to use java iterator instead of using looping functions to display entire array elements. Iterator enables to scan forward through any collection. Java iterator method returns an object that implements the iterator interface.
The primary purpose of a java iterator is to allow a user to process every element of a container while isolating the user from the internal structure of container. This will allows the container to store elements in any manner it wishes while allowing the user to treat it as if it were a simple sequence or list. Iterator class is usually designed in tight coordination with the respective container class.

Characteristics of Java Iterator
· Iterator interface is in the collection framework.
· It works similar to enumeration.
· Java Iterator traverses through all elements of the collection.
· List, Set interfaces have iterator() methods.
One important conceptual difference between iterators in the java collection library and iterators in other libraries is their style of accessing elements inside the array. In C++ iterators are modeled after array indexes, that means we need an array index i to traverse through the elements. Advancement of position is done by incrementing the array index as i++. Java iterators do not work like that, the look up and position change are tightly coupled, the only way to look up an element is to call next() and that loop advances the position.
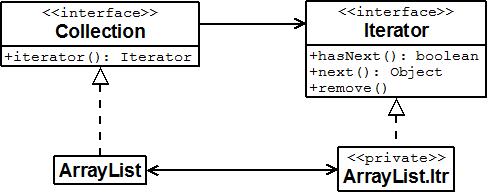

Using Java iterator interface
The java iterator interface has three fundamental methods:
Object next() : returns the next object to visit. It throws a NoSuchElementException if the end of the collection has been reached.
boolean hasNext() : returns true if there is another element to visit.
Object remove() : removes and returns the last visited object. The method will immediately follow an element visit. If the collection has been modified since the last element visit, then the method will throws an IllegaStateException.
Using hasnext() and next()
Repeatedly calling the next method, it is possible to visit the elements from the collection one by one. If the end of the collection is reached, the next method throws a NoSuchElementException. To avoid this situation, hasNext method should be called before calling next(). hasNext method returns true if the iterator object still has more elements to visit.
Iterator it=arraylis.iterator();
While(it.hasNext())
{
Object obj=it.next();
//code
}
Using remove()
remove() will removes the element that was returned by the last call to next. It is very much easy to remove an element if we know where it is. The iterator knows about positions in the collection, therefore the remove method was added to the java’s Iterator interface. The idea behind it is that if we need to remove one particular value, we have to see that element before we decide to remove it. If we decide to remove by position, we first need to skip past the element.
Removing the first element in a collection using java iterator
Iterator it=arraylis.iterator();
it.next(); //skip over the first element
it.remove(); //remove the first element now
Removing adjacent elements
it.remove();
it.next();
it.remove();
Sample code for java iterator program
import java.util.*;
public class iterators
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
List list=new ArrayList(); // Creating new list
int ar[]={1,2,3,4,5,6};
for(int i=0;i<ar.length;i++)
{
list.add(ari]); // adding elements to list
}
Iterator it =list.iterator();
While(it.hasnext())
{
system.out.println(it.next() + “\t”);
}}}
Output
1 2 3 4 5 6
Example program for using Java Iterator with array list
import java.util.*;
class samleiterator
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList Cities=new ArrayList(); //creating array list
Cities.add(New York); //adding elements to array list
Cities.add(Washington);
Cities.add(Beijing);
Cities.add(Dubai);
Cities.add(New Delhi);
Cities.add(Singapore);
System.out.println(“ Initial contents of Cities :”); //Displaying original contents of cities
Iterator it=Cities.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
Object obj=it.next();
System. Out.print(obj+ “ ”);
}
System. Out.println();
ListIterator lit=Cities.listIterator();
while(lit.hasNext() // modifying objects
{
Object obj=lit.next();
lit.set(obj+ “City”);
}
System.out.print(“Modified Cities:”); // Displaying modified objects using iterator
it=Cities.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
Object obj=it.next();
System.out.println(obj+ “ “);
}
System.out.println();
}}
Output
New York Washington Beijing Dubai New Delhi Singapore
New York City Washington City Beijing City Dubai City New Delhi City Singapore City
Was this java iterator tutorial useful?
If you feel this java iterator tutorial useful then vote up this article by clicking the green button below.
Do you have any doubts in java progamming feel free to ask me the doubts by posting queries in the comment column below.